
The adjustment of risk factors releases "hundred billion level" equity accumulation space! Shenwan Hongyuan: The insurance opening red is heating up, and the high dividend market is running ahead of schedule

Shenwan Hongyuan estimates that the adjustment of risk factors is expected to release "approximately 166.9 billion yuan of equity increase space" in the short term. The greater space for insurance funds to enter the market comes from the overall increase in their equity allocation ratio, and in the long term, there may even be "trillion-level" potential incremental funds. This policy is interpreted by the market as a catalyst for the "spring market," igniting trading enthusiasm for insurance "New Year opening," and may drive the high-dividend sector to start its rally ahead of schedule
A new regulatory rule targeting insurance funds is injecting new imaginative space into the A-share market.
According to the latest research report released by Shenwan Hongyuan Securities, regulatory authorities have recently lowered the risk factors for insurance companies' long-term holdings of certain equity assets. This move is expected to release a capital space of hundreds of billions in the short term and may become the catalyst for igniting the funding game in the "spring market."
This policy dynamic comes from the notice issued by the National Financial Regulatory Administration on December 5, 2025, titled "Notice on Adjusting the Risk Factors for Related Businesses of Insurance Companies." According to the notice, insurance companies that hold specific A-share targets and meet certain holding periods will have their applicable risk factors lowered when calculating solvency adequacy ratios.
In two reports released on December 6 and 7, Shenwan Hongyuan pointed out that this policy is a supporting measure to encourage long-term funds to enter the market. For some insurance companies, this constitutes "additional incentives for equity allocation." Analysts believe that in the current context where the large-scale economic and industrial catalysts are not yet clear, the logic of supply and demand for funds may become the main contradiction in the market, and the new regulations may just allow the trading expectations of "insurance opening red" to ferment.
Although the short-term boosting effect is significant, Shenwan Hongyuan also emphasized that the direct impact of this risk factor reduction is "marginal." In the long run, the true potential of insurance funds entering the market depends on the systematic increase in their overall equity allocation ratio, which has a "trillion-level" potential space behind it.
Calculation of Hundreds of Billions in Incremental Space: Short-term Marginal Boost, Long-term View on Allocation Ratio
The core of this policy is to "reduce the burden" for insurance companies' long-term holdings. Specifically, for stocks in the CSI 300 Index and the CSI Dividend Low Volatility 100 Index held for more than three years, the risk factor is lowered from 0.3 to 0.27; for ordinary shares listed on the Sci-Tech Innovation Board held for more than two years, the risk factor is lowered from 0.4 to 0.36.
Shenwan Hongyuan conducted a quantitative assessment of this. The report constructed three scenario assumptions: current, mid-term neutral, and mid-term optimistic. In the mid-term neutral scenario (assuming the long-term holding ratio returns to historical average levels), the minimum capital scale released by this risk factor adjustment is approximately 45.7 billion yuan. The report points out that "if the solvency adequacy ratio remains unchanged and the released minimum capital is invested in the same way," the additional stock investment scale could be approximately 166.9 billion yuan. In the optimistic scenario, this figure could reach 201.5 billion yuan.
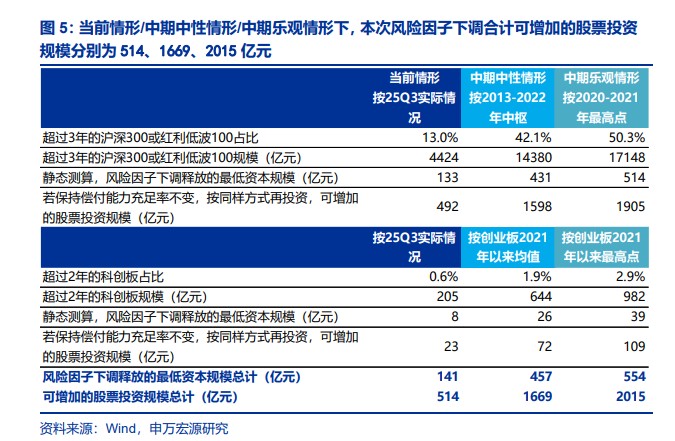
However, the report clearly states that this is only a "marginal impact." The greater imagination for insurance funds entering the market lies in the increase in their overall equity allocation ratio. Shenwan Hongyuan stated in the report, "The increase in the equity allocation ratio by insurance is the main source of the space for insurance funds to enter the market, with potential space at the trillion level."
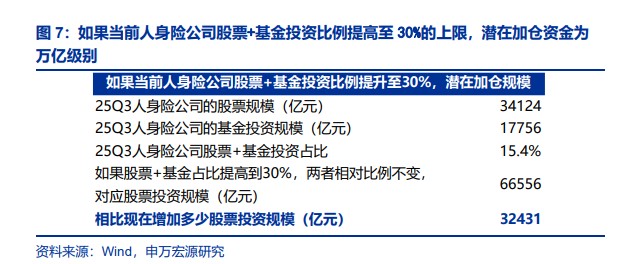
Data shows that as of the end of the third quarter of 2025, the proportion of stocks and funds invested by insurance companies exceeded 15%, still a considerable distance from the regulatory limit of 30%. According to Shenwan Hongyuan's static calculations, if current life insurance companies raise the investment ratio of stocks and funds to the 30% limit, assuming solvency adequacy ratios and other conditions are met, "an additional 3.2431 trillion yuan of stock investment could be increased." 。
Encouraging Long-term Investment to Alleviate Solvency Pressure
Shenwan Hongyuan analysis believes that the policy intention behind this risk factor adjustment is clear, mainly reflected in four aspects.
First, this is a "supporting policy to encourage long-term capital to enter the market." For state-owned insurance companies that have a high proportion of equity allocation by 2025, this move is a "lagging policy optimization"; for other insurance companies, it constitutes an additional incentive to increase equity allocation.
Second, the policy "further specifically encourages insurance funds to hold stocks in the CSI 300 and STAR Market," aiming to encourage insurance capital to maintain a high proportion of equity allocation in a normalized manner, while keeping necessary "tactical maneuvering space" through flexible holding time requirements.
Third, against the backdrop of the comprehensive implementation of the "Solvency II" framework approaching, lowering the risk factor helps alleviate the pressure on the comprehensive solvency adequacy ratio of some insurance companies.
Finally, the report emphasizes again that compared to the trillion-level potential brought by increasing the overall allocation ratio, the billion-level space released by this risk factor adjustment is only a marginal boost.

Insurance "New Year Opening" Heats Up, High Dividend Market May Start Early
At the market level, the timing of this policy's introduction is quite critical. Shenwan Hongyuan points out that in the context of a lack of clear industrial catalysts for the "spring market," "the influence of the supply-demand logic of funds may become the main contradiction."
The market was originally focused on the year-end public fund ranking competition and the layout rhythm of insurance capital's "New Year Opening." The report believes that the news of the risk factor adjustment may allow the "insurance New Year Opening competition to ferment accordingly."
The direct projection of this expectation is high dividend assets. With the replenishment of insurance capital and the enhancement of allocation willingness, high dividend sectors that combine stable dividends and defensive attributes may become their key allocation direction.
Shenwan Hongyuan reminds in the report, "The high dividend market is starting to run ahead," but also cautions investors that insurance capital's allocation of high dividends "will still strictly adhere to cost-effectiveness," and related transactions should pay attention to the rhythm of "buying expectations and selling realizations," with the competition likely mainly occurring before early 2026.
Regulatory Action: Lowering Risk Factors
Wallstreetcn reported that according to the notice issued by the National Financial Regulatory Administration on December 5, this risk factor adjustment mainly involves three aspects. The risk factors for stocks in the CSI 300 index and the CSI Dividend Low Volatility 100 index held by insurance companies for more than three years have been lowered from 0.3 to 0.27, with the holding time determined based on the weighted average holding time over the past six years The risk factor for ordinary shares listed on the Sci-Tech Innovation Board with a holding period of over two years has been adjusted down from 0.4 to 0.36, based on the weighted average holding period over the past four years.
In addition, the premium risk factor for export credit insurance business of insurance companies and the overseas investment insurance business of China Export & Credit Insurance Corporation has been adjusted down from 0.467 to 0.42, while the reserve risk factor has been adjusted down from 0.605 to 0.545.

Analysis suggests that this policy adjustment will cultivate and strengthen patient capital, encouraging long-term investment through differentiated settings, which is of positive significance for an active capital market.

