
T Medicine has been approved in the United States. Will the "Global Medicine King" be coming soon? The only obstacle is production capacity!

行业分析师预测,替尔泊肽可能成为有史以来最畅销的药物之一,年销售额将突破 500 亿美元,将超过诺和诺德的司美格鲁肽药物 Ozempic 和 Wegovy。
美东时间周三,礼来宣布旗下商品名为 Zepbound 的药物获得美国食品和药品管理局(FDA)批准,用于成年人的长期体重管理,预计今年底以前投放到美国市场。
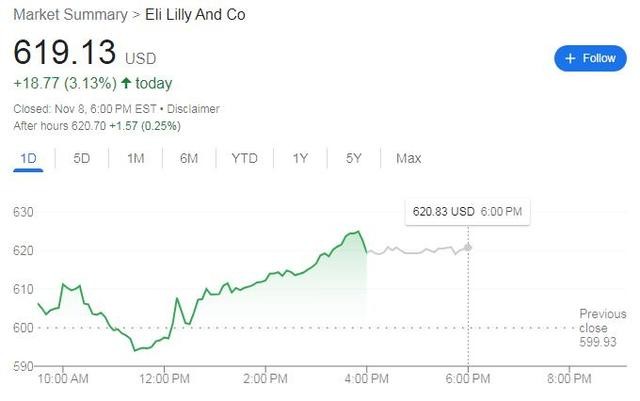
消息公布后,礼来股价涨幅持续扩大,尾盘接近 626 美元刷新日高时,日内涨超 4%,最终收涨 3.2%,收创历史新高。
Zepbound 含有被国内称为替尔泊肽(tirzepatide)活性成分。相关研究表明,替尔泊肽能产生比有” 减肥神药” 之称的司美格鲁肽 (semaglutide,旧称索马鲁肽) 更好的减肥效果。
行业分析师预测,替尔泊肽可能成为有史以来最畅销的药物之一,年销售额将突破 500 亿美元,将超过诺和诺德的司美格鲁肽药物 Ozempic 和 Wegovy。诺和诺德报告显示,到 2022 年,Ozempic 和 Wegovy 的销售额总计近 100 亿美元。
本次 Zepbound 获得 FDA 批准,帮助礼来确立了与诺和诺德分庭抗礼的地位,但能否超越诺和诺德,还需要解决一个关键问题——产能和供应。
替尔泊肽才是真正的药王?
实际上,礼来去年 5 月获批用于治疗 2 型糖尿病的创新药 Mounjaro 就是一种替尔泊肽药物。据媒体此前报道,由于 Wegovy 的供应限制,先前已有一些美国人使用 Mounjaro 减肥。
替尔泊肽是葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽(GIP)和胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)的双受体激动剂。它将两种肠促胰素的作用整合到一个分子中,每周注射一次。
GIP 能够补充 GLP-1 受体激动剂的作用。在临床前模型中,已证明 GIP 可减少摄食量并增加能量消耗,从而减轻体重,当联合 GLP-1 受体激动剂时,可能对葡萄糖水平和体重产生更大的影响。
相关试验显示,替尔泊肽的减肥效果比司美格鲁肽更好。
根据礼来公司 4 月下旬公布的早期研究结果,Mounjaro 在近 17 个月的时间里,帮助超重或肥胖的糖尿病患者减轻了 16% 的体重,即超过 34 磅。司美格鲁肽的服用者在 16 个月内减轻了约 15% 的体重。
后期研究进一步证明了替尔泊肽的减肥效果:非糖尿病患者在每周注射该药物的情况下,体重减轻了 22%。对于服用最高剂量的典型患者来说,这意味着减掉 50 磅以上的体重。
礼来公司肥胖临床开发医学总监 Nadia Ahmad 博士说,糖尿病使减肥变得非常困难,这意味着后期研究尤其重要。她说:"我们从未见过这种程度的减重效果。"
最后的对决:产能!
本次 Zepbound 获得 FDA 批准,帮助礼来确立了与诺和诺德分庭抗礼的地位,但能否超越诺和诺德,最后还要解决关键的产能和供应问题。
由于减肥药需求巨大,Wegovy、Ozempic 和 Mounjaro 这三种药物的不同剂量都曾出现在 FDA 短缺药物名单上。
华尔街见闻文章《FDA 警告:减肥神药缺货严重 | 见智研究》也提到,司美格鲁肽全球缺货已经持续接近一年,并且还将持续缺货。
诺和诺德已经限制了 Wegovy 较低剂量的供应,以确保已经在用这种药的人能持续获得供应,满足現有患者需求预计需要数年时间。
礼来和诺和诺德正投入数十亿美元扩大减肥药的产能。
礼来在北卡罗莱纳州建设两座工厂,投资 40 亿美元,力争在 2023 年底前使含有替尔泊肽的肠外肽类药物产量提高一倍。
其中一座工厂位于达勒姆三角研究园区,已经开始生产。该工厂使用高速自动化、无人驾驶车辆和机械臂,为 Mounjaro 生产自动注射器。该工厂也正在准备进行产品制剂,将活性成分替尔泊肽与其他成分混合,制成成品药物,然后注入注射器。
礼来表示,为满足需求,该工厂每周 7 天、每天 24 小时连轴运行。尽管如此,据礼来制造运营总裁 Edgardo Hernandez 介绍,合成替尔泊肽需要数月时间,因为它需要进行一系列将氨基酸连接成肽链的化学反应,还需要提纯和品质控制。
“我们正在努力实现大规模生产,” 他说,“我们正在积极增设产能。”
诺和诺德首席执行官 Lars Fruergaard Jorgensen 8 月接受媒体采访时表示:“由于短缺,有些人可能会认为我们没有生产任何产品,但我们拥有该类别中最受欢迎的产品之一,并且正在以两位数的百分点增长。”“所以我们正在大幅增加(产能),并且我们将在未来几年进行大量投资。”
这些投资预计将获得数倍的回报。根据投资公司 BMO 资本市场的估计,到 2035 年,肥胖药物将在全球范围内带来 1000 亿美元的年收入。

